

Tanjungpura University Chemistry postgraduate students again held a public lecture with the theme: Metal Oxidation Modification in Waste Remediation, presented by Diana Rakhmawaty Eddy. He is a lecturer at the Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences, Padjadjaran University, Bandung.
Talking about waste is endless as long as humans are still producing and consuming things. There is always factory or industrial and other waste that is dumped into the environment, which cannot be naturally processed by the environment itself into a simpler and more stable form. One of the dangerous wastes is metal waste such as Hg (mercury), Pb (lead), As (arsenic), Ni (nickel), Cr (chrome). This is where the role of researchers is to develop compounds that can reduce metal levels in the environment.
Mrs. Diana and her two colleagues, Iman Rahayu and Kemal Handani conducted research on a Gd/TiO2 Nano Particle Photo Catalyst which functions to reduce levels of the metal Cr (VI) which is very dangerous for the environment and humans because it will cause a deadly disease if exposed to the human body. .
Why did Diana's research focus on Cr (VI)? The decrease in Chromium (VI) levels is very critical and a solution must be sought immediately. Mrs. Diana explained that based on studies, the element Cr(VI) can disrupt the function of the liver, heart, brain and kidneys, causing cancer and death. Because these metal elements become radicals in the body. Reducing Cr (VI) levels using TiO2 photocatalyst for several reasons, namely easy to obtain, non-toxic or safe for the environment and stable to light.
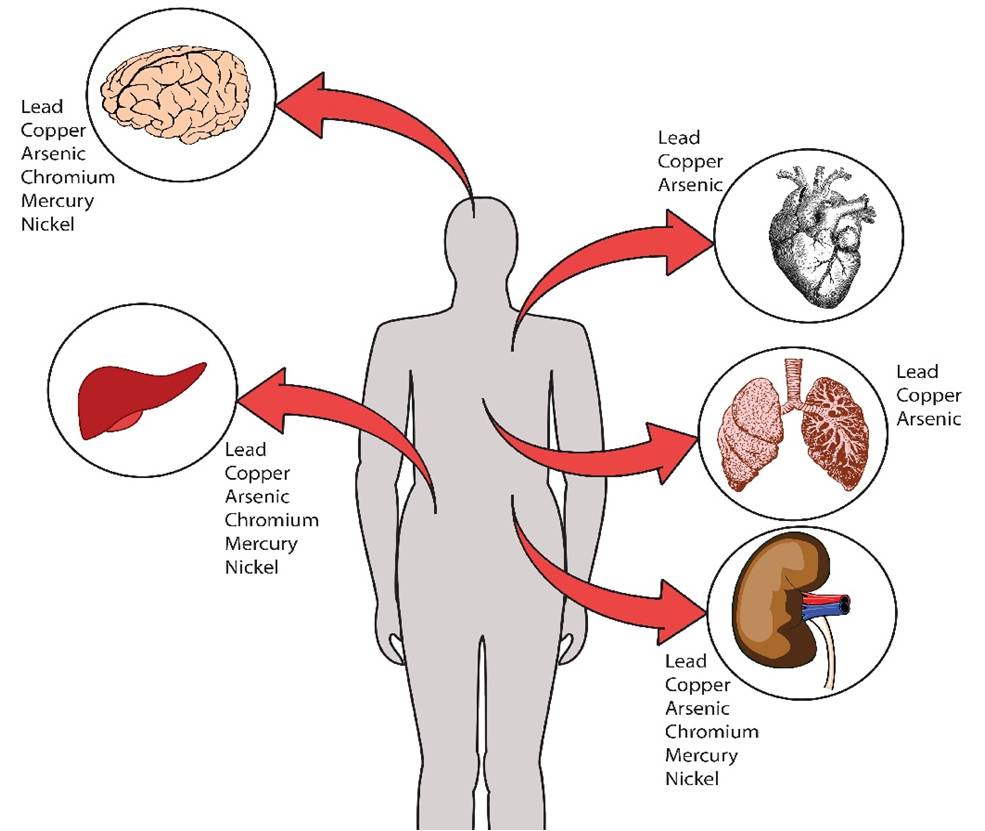
Danger of Cr (VI) on organs in the human body
Mrs. Diana's research certainly had complicated stages. Starting from the synthesis of TiO2 photocatalyst, doping TiO2 with Gd, then TiO2 was characterized using XRD and SEM-EDX instruments, then Gd/TiO2 photocatalyst activity was tested on Cr(VI) metal samples, then Cr(VI) content was analyzed before and after the addition of photocatalysis which has been made. The results were quite satisfactory, Cr(VI) levels were reduced by 93.72% using 1% Gd/TiO2 photocatalyst irradiated for 1 hour.
Apart from making Photocatalysts, Mrs. Diana also explained her success in the synthesis and characterization of Titanium (IV) Oxide-gadolinium as photocatalysis to reduce the Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) Carbosulfan figures. Where COD is an indicator of chemical water pollution. COD indicates the total amount of oxygen required to chemically oxidize organic materials. The more polluted the waters, the higher the COD value. And all of this comes from waste. Both household waste, industrial waste, livestock waste and other waste.
The role of Physical and Inorganic Chemistry in processing waste and reducing metal levels in waste has been going on for many years. Akademika always tries to find the best solution, both in terms of time, cost and quantity, to continue to reduce waste as an effort to care for the environment. Ms. Diana and her colleagues' research was shared with postgraduate students in the Chemistry department. Interested in caring for the environment like Mrs. Diana? Let's join the postgraduate Chemistry program at FMIPA Tanjungpura University (Pontianak, 4 May 2018).